Articles
October 23, 2023
Share post:
Balancing Transparency and Privacy: The Revolutionary Role of Zero-Knowledge Proofs in Blockchain
The essence of blockchain technology is trust via transparency. Every participant can verify transactions and states without the need for a central authority. However, this transparency can sometimes be at odds with the requirement for privacy. Enter zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs), a cryptographic method that enhances privacy and confidentiality without compromising the trust and security characteristics intrinsic to blockchains.
Understanding Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs)
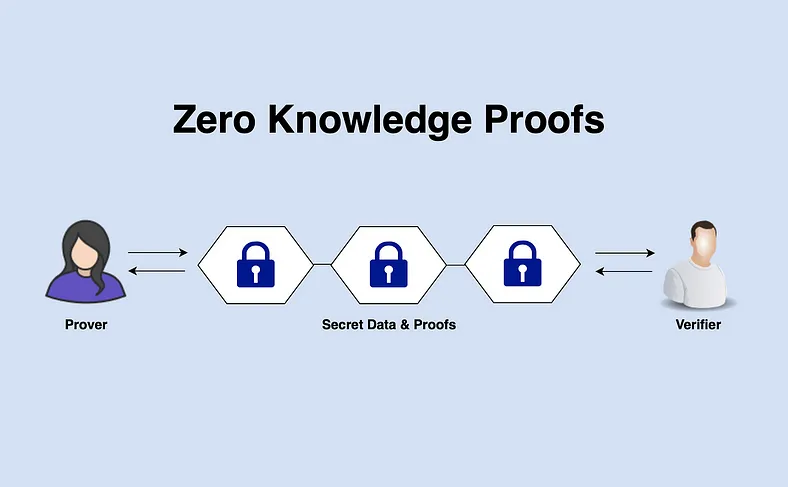
Zero-knowledge proofs are cryptographic protocols that allow one party, known as the prover, to demonstrate to another party, called the verifier, that a statement is true without revealing any information about the statement itself.
In technical terms, a ZKP must satisfy three properties:
Completeness: If the statement is true, the honest prover can convince the verifier of its truth.
Soundness: If the statement is false, a cheating prover cannot convince the honest verifier that it’s true.
Zero-knowledgeness: If the statement is true, the verifier learns nothing other than the validity of the statement.
Integration with Blockchain: zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs

Two prominent forms of ZKPs that have been integrated into blockchain technology are zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge) and zk-STARKs (Zero-Knowledge Scalable Transparent Argument of Knowledge).
zk-SNARKs: These are non-interactive proofs where the prover can demonstrate possession of certain information without revealing it. Their “succinctness” ensures that the proofs are small in size and can be verified quickly, a critical requirement for scalable blockchain systems. zk-SNARKs, however, rely on a trusted setup, which can be a potential point of vulnerability.
zk-STARKs: An evolution over zk-SNARKs, zk-STARKs do not require a trusted setup and offer quantum resistance. However, they demand more computational resources and generate larger proofs.
Applications in Blockchain
Transaction Privacy: Platforms like Zcash utilize zk-SNARKs to provide shielded transactions, where the transaction details (sender, recipient, amount) are obscured, but the network can still validate their legitimacy.
Scalability Solutions: ZKPs can bundle multiple transactions into a single proof, known as roll-ups, significantly reducing the data each transaction needs on-chain. Ethereum, for example, has looked into zk-rollups as a potential scalability solution.
Identity Verification: ZKPs allow for identity verification without revealing underlying personal details. Users can prove they are above a certain age, have enough funds, or possess a valid ticket without revealing birthdates, exact account balances, or ticket numbers.
Interoperable Chains: In multi-chain environments or sidechains, ZKPs can be used to prove the state of one chain to another without revealing the specifics of individual transactions, facilitating secure and private interoperability.
Gaming: Zero-knowledge proofs are beginning to reshape the gaming industry. Privacy-powered games leverage zk-SNARKs to provide players with enhanced confidentiality. Aleo, a platform dedicated to promoting privacy in decentralized systems, highlights the potential of ZKPs in gaming. These cryptographic methods enable game developers to incorporate elements like private leaderboards, confidential multiplayer interactions, and secret game states. This not only enhances user privacy but also provides a fresh layer of immersive gameplay. For instance, mystery or detective games could benefit from ZKPs by ensuring that the game state remains a secret, allowing players to genuinely experience the thrill of uncovering clues and solving mysteries without any spoilers.
Ads: In the realm of digital advertising, user privacy is a growing concern. Advertisers need insights into user preferences to display relevant ads, but this often comes at the cost of user privacy. With zero-knowledge proofs, it’s possible to strike a balance. Advertisers can obtain proof that a user belongs to a particular demographic or has specific interests without accessing the underlying personal data. This ensures that users see relevant ads without compromising their private information. For instance, a user could prove they’re interested in travel without revealing their recent searches, ensuring they receive travel-related ads without risking their data privacy.
The Future of Gaming with ZKPs

Drawing from the insights provided by Aleo, it’s evident that zero-knowledge proofs have the potential to revolutionize the gaming industry. One of the primary advantages of integrating ZKPs into games is the ability to authenticate actions and achievements without compromising gameplay secrets. Players can validate their scores, prove completion of certain challenges, or verify in-game purchases, all while maintaining the confidentiality of their game state.
Furthermore, privacy-powered games can mitigate common issues in the gaming world, such as cheating or exploiting game mechanics. By leveraging zk-SNARKs, game developers can ensure that all player actions are legitimate without revealing the specifics of those actions. This not only ensures a level playing field but also amplifies the gaming experience by adding an element of mystery and unpredictability.
In essence, as the gaming industry continues to evolve and players become more conscious of their digital privacy, the incorporation of zero-knowledge proofs into game mechanics and systems will likely become a standard, offering both enhanced gameplay experiences and robust privacy measures.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
While ZKPs offer immense potential, they come with challenges:
Computational Intensity: Especially with zk-STARKs, the generation and verification of proofs can be computationally demanding.
Complexity: Implementing ZKPs requires deep cryptographic expertise, making it a challenge for many projects to adopt.
Standardization: As with many emerging technologies, there’s a need for standard protocols and practices to ensure compatibility and security across different implementations.
In conclusion, zero-knowledge proofs represent a pioneering frontier in the blockchain sector, promising to reconcile the often conflicting demands of transparency and privacy. As research progresses and the technology matures, ZKPs are poised to become a fundamental pillar in the next generation of decentralized systems.
Share post:



